DUBBAH
Welcome to the website for the project DUBBAH.
From this site you can read about:
- What is DUBBAH
- The project background
- Media and publicity
- The data
- The results of the project
- The software source code
Welcome to the website for the project DUBBAH.
From this site you can read about:
DUBBAH is an acronym for Digital Understøttet Bedre Brug Af Hjælpmidler which can be translated to digital supported better usage of assistive technology.
It is a project funded by Kommunernes Landsforening which focuses on developing publicly available machine learning algorithms that can
assist providers in the management of loaning assistive technology.
The objectives are:
The Danish Social Security Administration has formerly investigated the effects of early rehabilition in the proces of loaning assistive technology. In a project called "Tidlige Rehabiliterende Indsats (TRI)", which can be downloaded here, they found different patterns in the loans of assistive technologies depending on what a citizen applied for in the beginning. As an example citizens who applied to have their doorstep removed very often was in need of more help. They also found that any improvement regarding self capacity and physical capacity gained as an effect of assistive technology or exercise varied depending on age and the baseline.
The program for healhtcare technology was founded by the municipalities in Denmark. The objective were to ensure a strategical developement of healthcare tehcnology such as how to promote sharing of knowledge, coordination, common documentation and implementation of new healthcare technology. You can read more about the program here. In the status report from 2017, which can be accessed here, it can be seen that "better usage of assistive technology" was rated among the top 5 health tech contributers in the past and in the future. They define better usage as ways to promote collaboration and effictivity in between, occupational therapist, physical theprapist, nurses and the citizen. Furthermore, the program focuses in 2018 on healthcare technology for mobility that can rehabilitate, maintain or promote self capacitity in the citizen.
The potential benefits of artifical intelligence within healthcare are often discussed in novel science and research literature. Some of the hopes are that technology can help overcome future demographic challenges by being applied in a broad range of fields such as cardiology, radiology and much more (Zhang 2018). As an example apple recently published the new generation of Apple watch which is capable of detecting ateria fibrillation. One of the huge benefits of medical data is the size. In 2020 medical health records are predicted to generate 25000 petabytes of data (Feldman 2012). Nonetheless, the practical application of big data and machine learning in healthcare is still somewhat rudimentary (Peterson 2018). In a review from 2016 the challenges and oppertunities of big data were discussed. Some of the drawbacks identified were data quality, data security, privacy, interoperability etc. (Toldo 2016). Petersen et al. describe different challenges for patients / developers / healthcare professionals. They suggest a framework for the stakeholder relastionships requiring complex and cooperative collaboration between all stakeholders. Similar solution including interdisciplinary development was proposed in a recent review investigating how digital healthcare can be used within epidemiology (Widmer 2018). This is exactly what we strive for in DUBBAH.
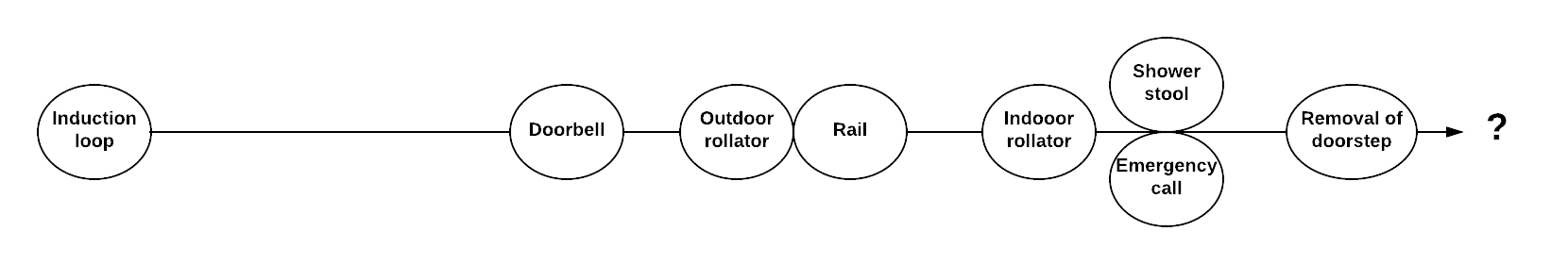
The following case story is authentic and taken from Aalborg Municipality. In order too keep it anonymous the patient is called "Mr.Jensen".
In 2006 was "Mr. Jensen" loaned an Induction loop.
In October 2014, he was granted a stronger doorbell with puzzle call.
In November 2014, he was given an outdoor rollator and a month after that a rail for self-lifting.
In May 2015, an indoor rollator and two months later, he gets a shower stool and a GSM emergency call, if he falls over.
At the beginning of 2018 he gets the doorsteps removed in his home.
Looking at Mr.Jensen's self-reliance it is clear that it has a negative development.
The rate of which assistive technologies are granted is increasing from November and onwards.
A timeline of this might look like this:
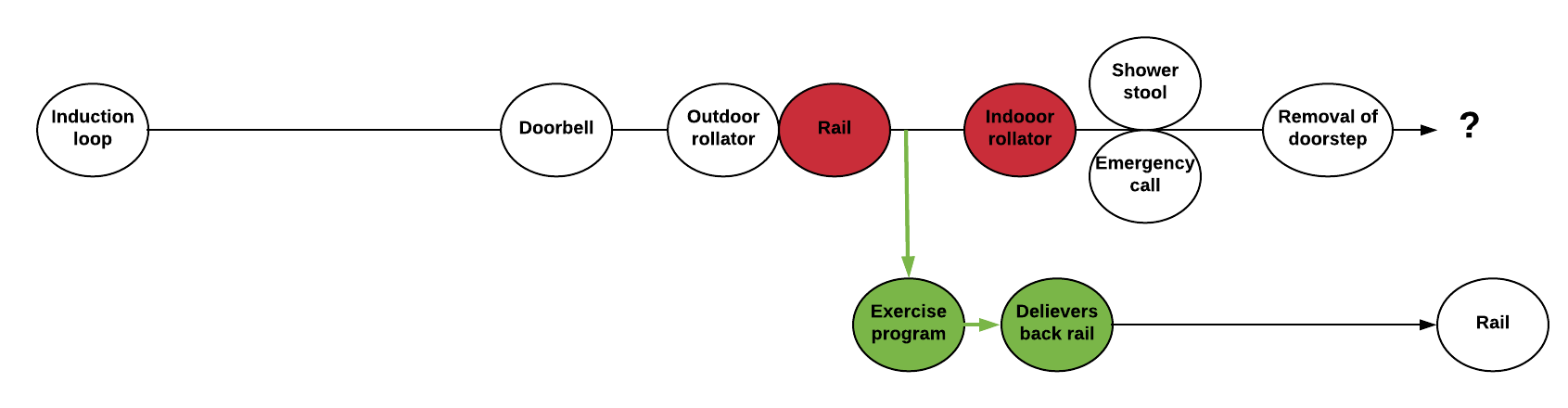
In an article published the 11th of December 2018 by The Association of Danish Physiotherapists they talk about everyday problems in the management of assistive technologies. They argue that more citizens are often not granted the right assistive technology and thus more people file complaints to the council of appeal. In 2017 every 3rd reported complaint was successfull - this is a remarkle increase from the years before. Hence, the danish associations for physiotherapists and occupational therapists wrote to the minister regarding this topic. The minister agreed to discuss how assistive technologies are managed, but guaranteed no more money would be granted. You can read the answer here.
Here you can read what other medias say about the project.


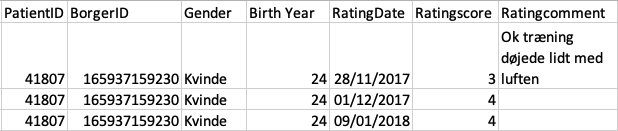
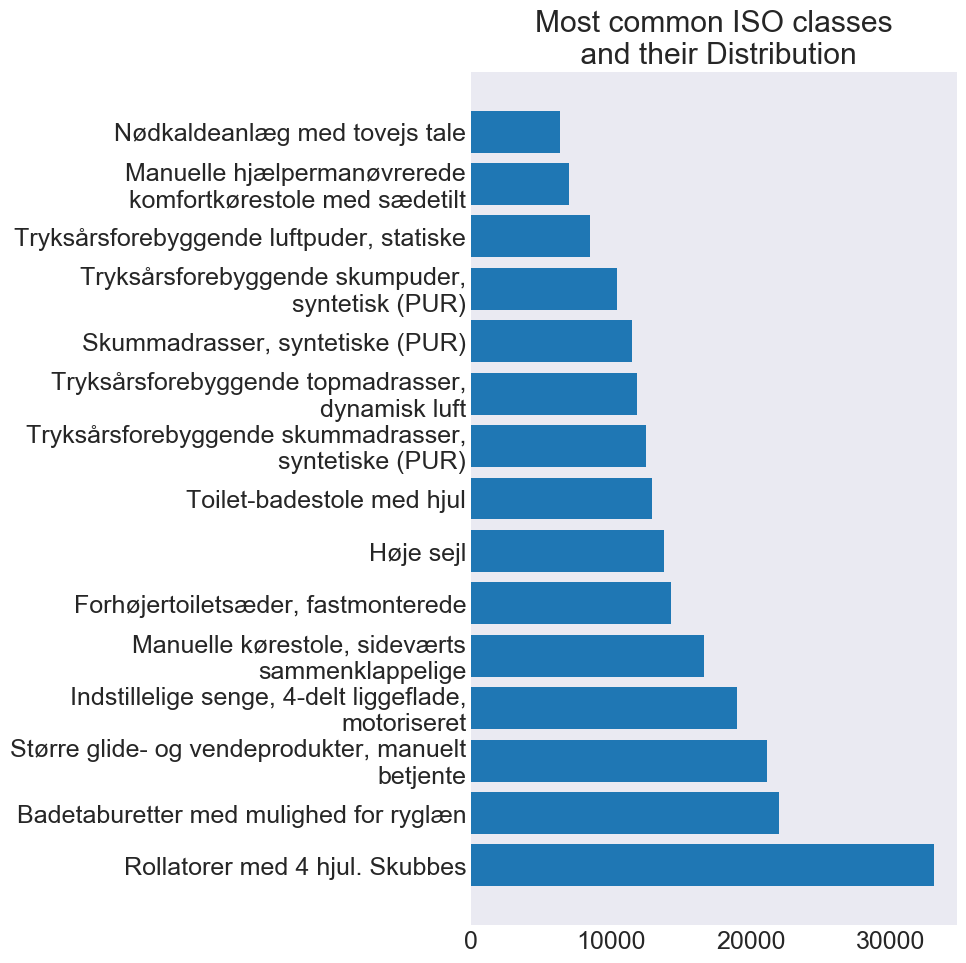
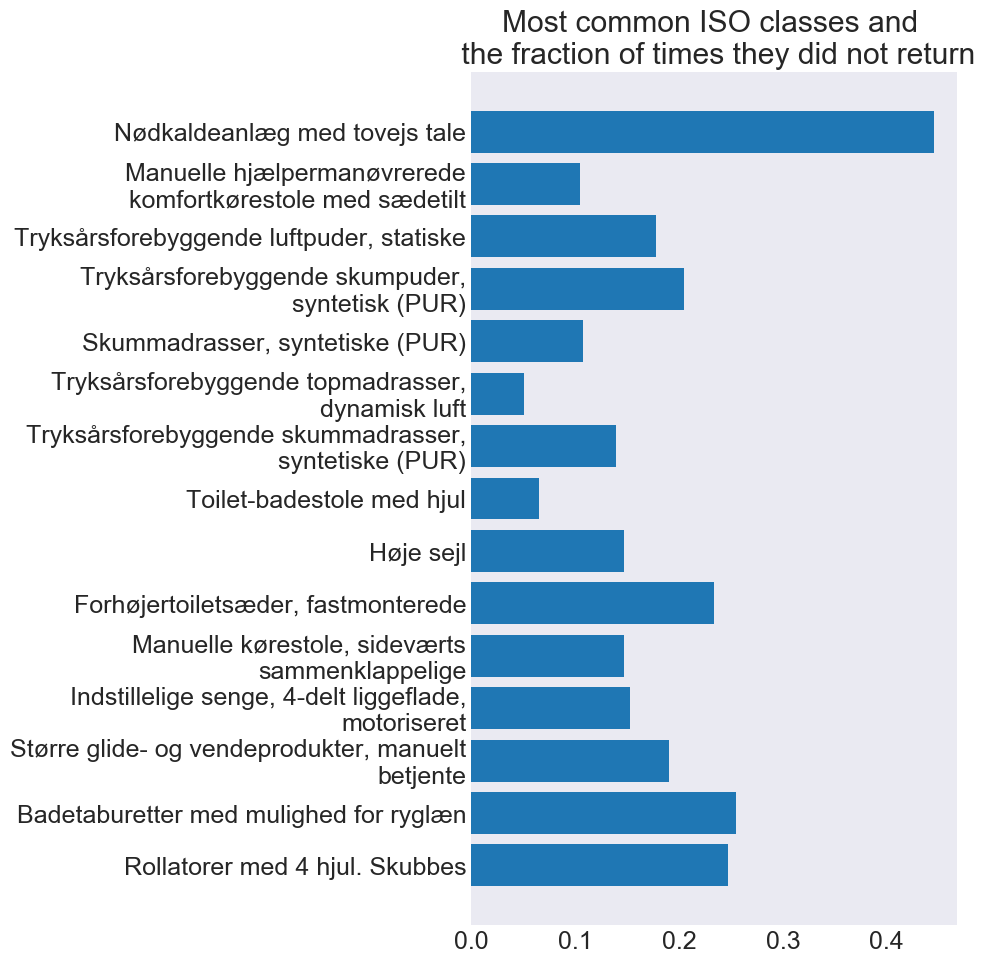
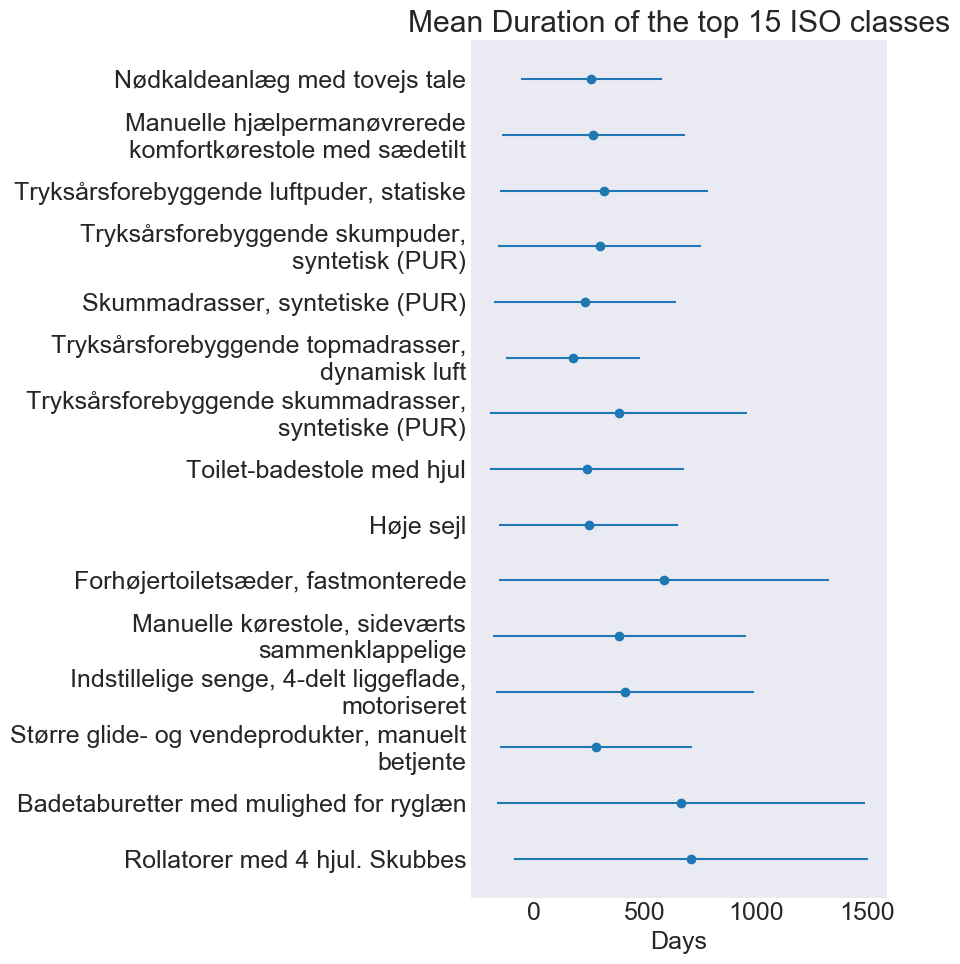
This section will be updated continously as new results are discovered.
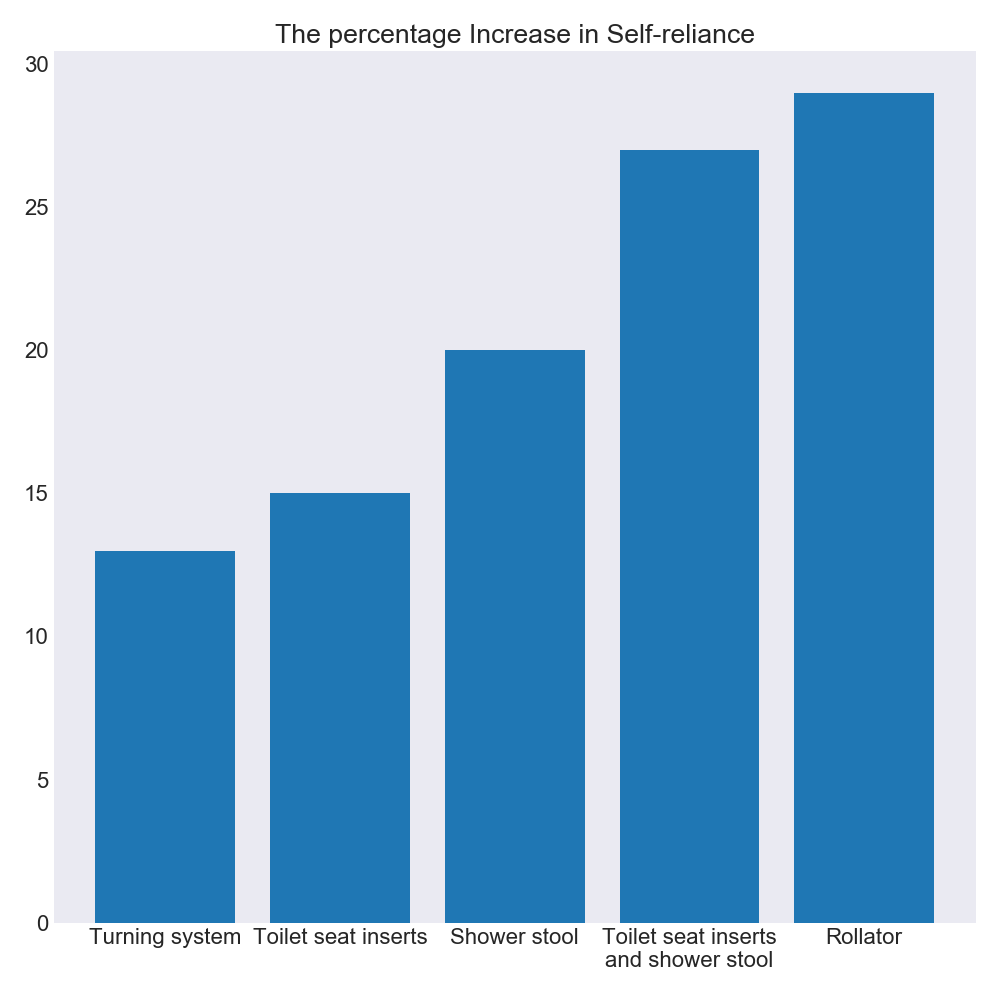
In the data collection phase some preliminary experiments were conducted. It was identified that evaluated by self-reliance the mean increase from physical exercise was 14% when adjusting for sickness. More interestingly differences in the outcome based on assistive technologies were found much in compliance with the study from Fredericia Municipality. The results showed that citizens using rollators achieved the highest increase at 29% and citizens using tuning system the lowest at 13 % as seen in the bar chart below.